Which Of The Following Statements Is Best Supported By The Data In The Ndvi And Chlorophyll Folder?
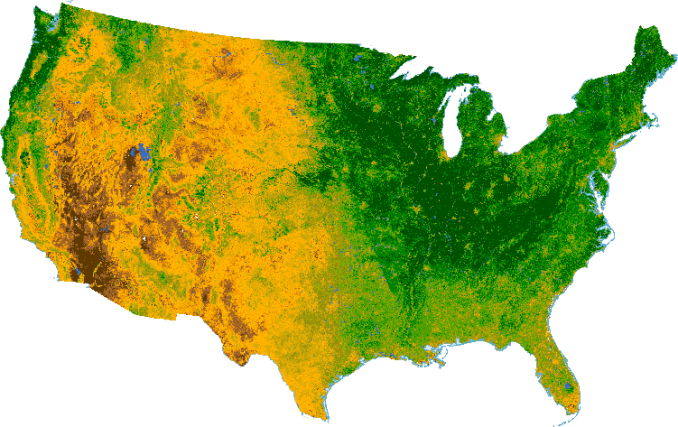
"Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) quantifies vegetation by measuring the difference between almost-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and red light (which vegetation absorbs)."
What is NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index)?
NDVI always ranges from -ane to +i. Simply there isn't a distinct boundary for each type of land comprehend.
For example, when you have negative values, information technology's highly likely that it's water. On the other hand, if you accept an NDVI value close to +one, there'south a high possibility that it's dumbo green leaves.
But when NDVI is shut to zero, there are likely no green leaves and it could even be an urbanized surface area.
NDVI is the almost common alphabetize that analysts use in remote sensing. But how practise you calculate it? What practise NDVI values represent? How practise Earth scientists use NDVI?
How do you calculate NDVI?
As shown below, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) uses the NIR and red channels in its formula.
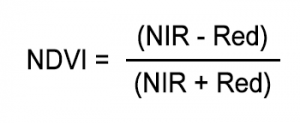
Good for you vegetation (chlorophyll) reflects more than near-infrared (NIR) and dark-green light compared to other wavelengths. Just information technology absorbs more than reddish and blue lite.
This is why our eyes see vegetation as the color light-green. If you could see about-infrared, then it would be potent for vegetation too. Satellite sensors like Landsat and Sentry-2 both accept the necessary bands with NIR and red.
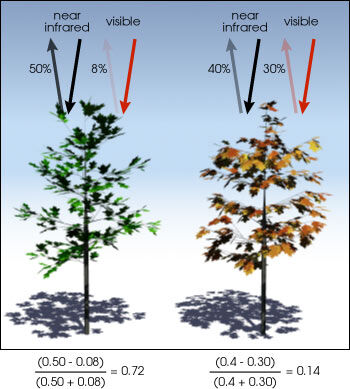
The consequence of this formula generates a value betwixt -1 and +1. If you have depression reflectance (or depression values) in the red channel and high reflectance in the NIR channel, this will yield a loftier NDVI value. And vice versa.
Overall, NDVI is a standardized way to measure healthy vegetation. When you have high NDVI values, you have healthier vegetation.
When yous have low NDVI, you have less or no vegetation. Generally, if you desire to see vegetation modify over time, and then you lot will accept to perform an atmospheric correction.
Case of NDVI in agriculture
Allow's examine NDVI for an agronomical area with center pivot irrigation. Pivot irrigation rotates on a bespeak creating a circular crop pattern.
In truthful color, here'southward how it looks for red, green, and blue bands. We say true color considering it is the aforementioned as how our eyes see.

In the formula, you can see how NDVI leverages about-infrared (NIR). And so when nosotros put the NIR band to display equally red, we go color infrared. Nosotros say colour infrared because near-infrared is in the ruby-red channel. As you tin can see beneath, the pivot irrigation vegetation should already exist shouting out at you in bright crimson!
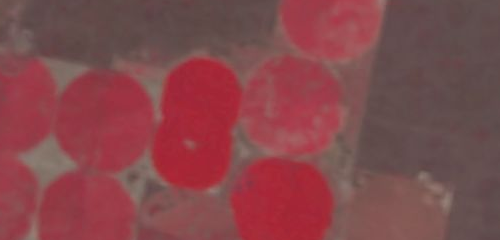
When you employ the formula, bright green indicates high NDVI. Whereas cherry has low NDVI. So it's quantifying vegetation by measuring the divergence between nearly-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and cherry-red light (which vegetation absorbs).

As you can see, information technology's easy to selection out the pivot irrigation circles using NDVI. It makes it easier to allocate because of NDVI.
How do we use NDVI?
We see several sectors using NDVI. For instance, in agriculture, farmers use NDVI for precision farming and to measure biomass.
Whereas, in forestry, foresters use NDVI to quantify wood supply and leaf area index.
Furthermore, NASA states that NDVI is a practiced indicator of drought. When water limits vegetation growth, it has a lower relative NDVI and density of vegetation.
In reality, there are hundreds of applications where NDVI and other remote sensing applications are existence applied in the existent globe.
Which satellite imagery has near-infrared for NDVI?
Every bit mentioned before, satellites like Scout-ii, Landsat, and SPOT produce ruby-red and about infrared images.
This list of 15 costless satellite imagery data sources has data that you lot can download and create NDVI maps in ArcGIS or QGIS.
For example, we use NDVI in agronomics, forestry, and the environment.
Do yous know any applications using NDVI?
Which Of The Following Statements Is Best Supported By The Data In The Ndvi And Chlorophyll Folder?,
Source: https://gisgeography.com/ndvi-normalized-difference-vegetation-index/
Posted by: leenegards40.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Statements Is Best Supported By The Data In The Ndvi And Chlorophyll Folder?"
Post a Comment